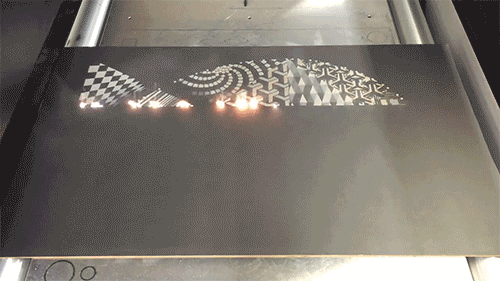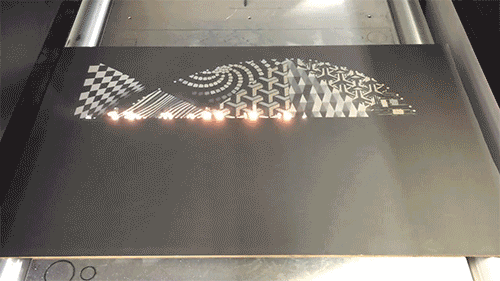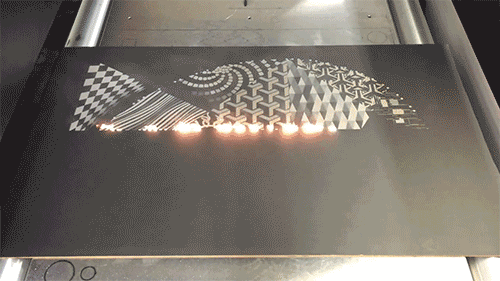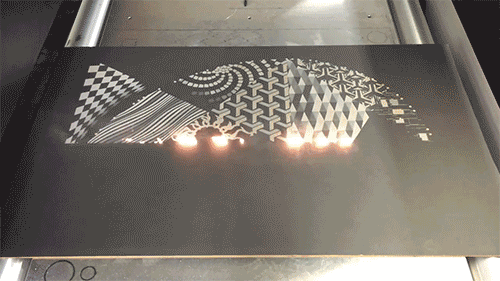
Laser engraving
Laser engraving, also called laser engraving or laser marking, is a process of surface treatment using optical principles. The laser beam is used to carve a permanent mark on the surface of the material or the inside of the transparent material. The laser beam can produce two kinds of chemical effects and special effects on matter. When the substance instantly absorbs the laser light, it produces a physical or chemical reaction, thereby engraving traces or displaying patterns or text.
Electroplating
Electroplating is the process of plating a thin layer of other metals or alloys on the surface of certain metals by using the principle of electrolysis. It is the process of using electrolysis to attach a layer of metal film to the surface of metal or other materials to prevent Metal oxidation (such as rust), improve wear resistance, electrical conductivity, reflectivity, corrosion resistance (copper sulfate, etc.) and enhance aesthetics. The outer layer of many coins is also electroplated.

Mechanical polishing
Mechanical polishing is a polishing method that relies on cutting and plastic deformation of the material surface to remove the polished convex parts to obtain a smooth surface. Generally, oil stone strips, wool wheels, sandpaper, etc. are used, and manual operations are the main ones. Special parts such as the surface of the rotating body. Auxiliary tools such as turntables can be used, and ultra-precision polishing methods can be used for high surface quality requirements. Ultra-precision polishing is the use of special abrasive tools, which are pressed tightly on the processed surface of the workpiece in a working fluid containing abrasives for high-speed rotation. Using this technology, the surface roughness of Ra0.008μm can be achieved, which is the highest among various polishing methods. Optical lens molds often use this method.

EDM
Electric discharge machining is a special machining method that uses the electric erosion effect produced by the pulse discharge between the two electrodes immersed in the working fluid to ablate conductive materials, also known as electric discharge machining or electro-erosion machining. Tool electrodes are commonly used electro-corrosion-resistant materials with good conductivity, high melting point, and easy processing, such as copper, graphite, copper-tungsten alloy, and molybdenum. During the machining process, the tool electrode is also lost, but it is less than the amount of metal erosion of the workpiece, and even close to no loss.
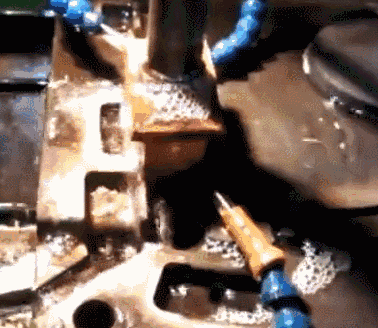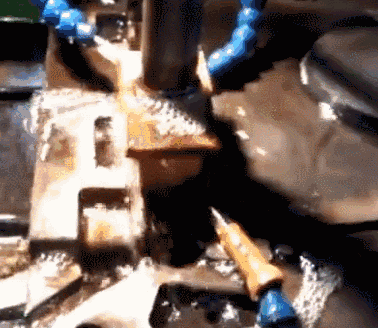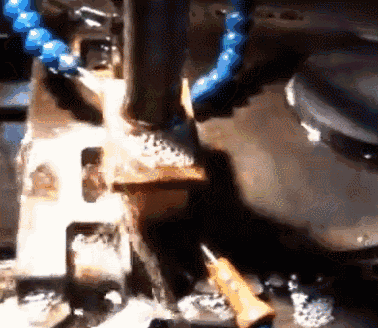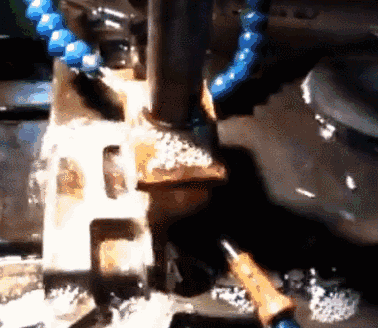
Electrolytic polishing
Electrolytic polishing uses the polished workpiece as the anode and the insoluble metal as the cathode. The two electrodes are immersed in the electrolytic cell at the same time, and the DC ionization reaction produces selective anode dissolution, so as to achieve the effect of removing fine burrs on the surface of the workpiece and increasing the brightness.
Chemical polishing
Chemical polishing is a method of removing wear scars and eroding and leveling by the selective dissolution of chemical reagents on the uneven areas of the sample surface.


Zinc plating
Zinc plating refers to a surface treatment technology that coats a layer of zinc on the surface of metals, alloys or other materials for aesthetics and rust prevention.

Spraying
Spraying A spray gun or dish atomizer, with the help of pressure or centrifugal force, is dispersed into uniform and fine droplets and applied to the surface of the object to be coated. It can be divided into air spraying, airless spraying, electrostatic spraying and various derived methods of the above basic spraying forms, such as large flow and low pressure atomization spraying, thermal spraying, automatic spraying, multi-group spraying, etc.
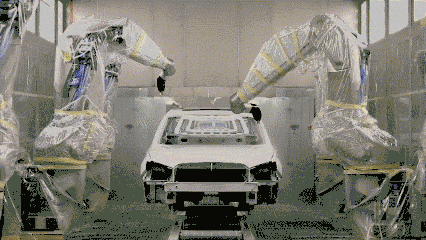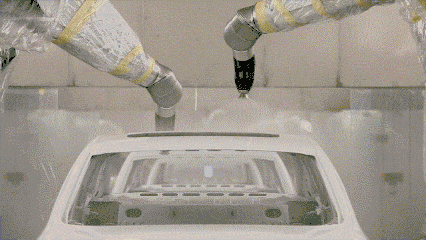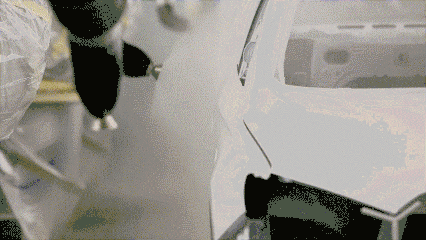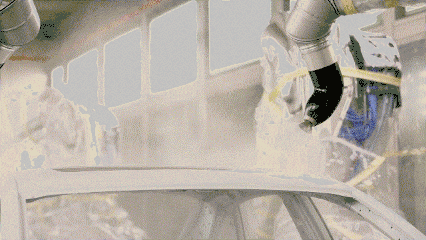
Powder spraying
Powder spraying is the use of powder spraying equipment (electrostatic spraying machine) to spray powder coating on the surface of the workpiece. Under the action of static electricity, the powder will be uniformly absorbed on the surface of the workpiece to form a powdery coating; the powdery coating is baked at a high temperature Baking, leveling and curing, it becomes the final coating with different effects (different types of powder coating effects).

Microarc oxidation
Microarc oxidation (MAO), also known as microplasma oxidation (MPO), is the instantaneous high temperature generated by arc discharge on the surface of aluminum, magnesium, titanium and its alloys through the combination of electrolyte and corresponding electrical parameters. Under high pressure, a ceramic film mainly composed of base metal oxide is grown.

Metal wire drawing
Metal wire drawing is the manufacturing process of repeatedly scraping aluminum plates out of lines with sandpaper. The main process flow is divided into three parts: de-esterification, sand mill, and water washing. In the wire drawing process, the special coating technology after anodizing can generate a coating layer containing the metal component on the metal surface, clearly showing every tiny wire mark, so that the metal matte is full of fine hair strands. luster.

Frosting
Frosting is a process in which the original smooth surface of the object becomes matte, so that the light is irradiated on the surface to form a diffuse reflection. The frosting treatment in chemistry is to mechanically or manually grind the glass with abrasives such as emery, silica sand and pomegranate powder to make a uniform and rough surface. It can also be processed with hydrofluoric acid solution on the surface of glass and other objects. The product becomes frosted glass.






